commit-to-git
Commit to Git Repository
You can commit the generated changelog file to your git repository using the Run Command step in the pipeline. This allows you to version control your changelog file and keep track of changes over time. Otherwise, once the pipeline is executed, pods will be deleted and the changelog file will be lost.
- In the Pipeline, under the
Step Groupsection, add a new stepRun Commandas the step type.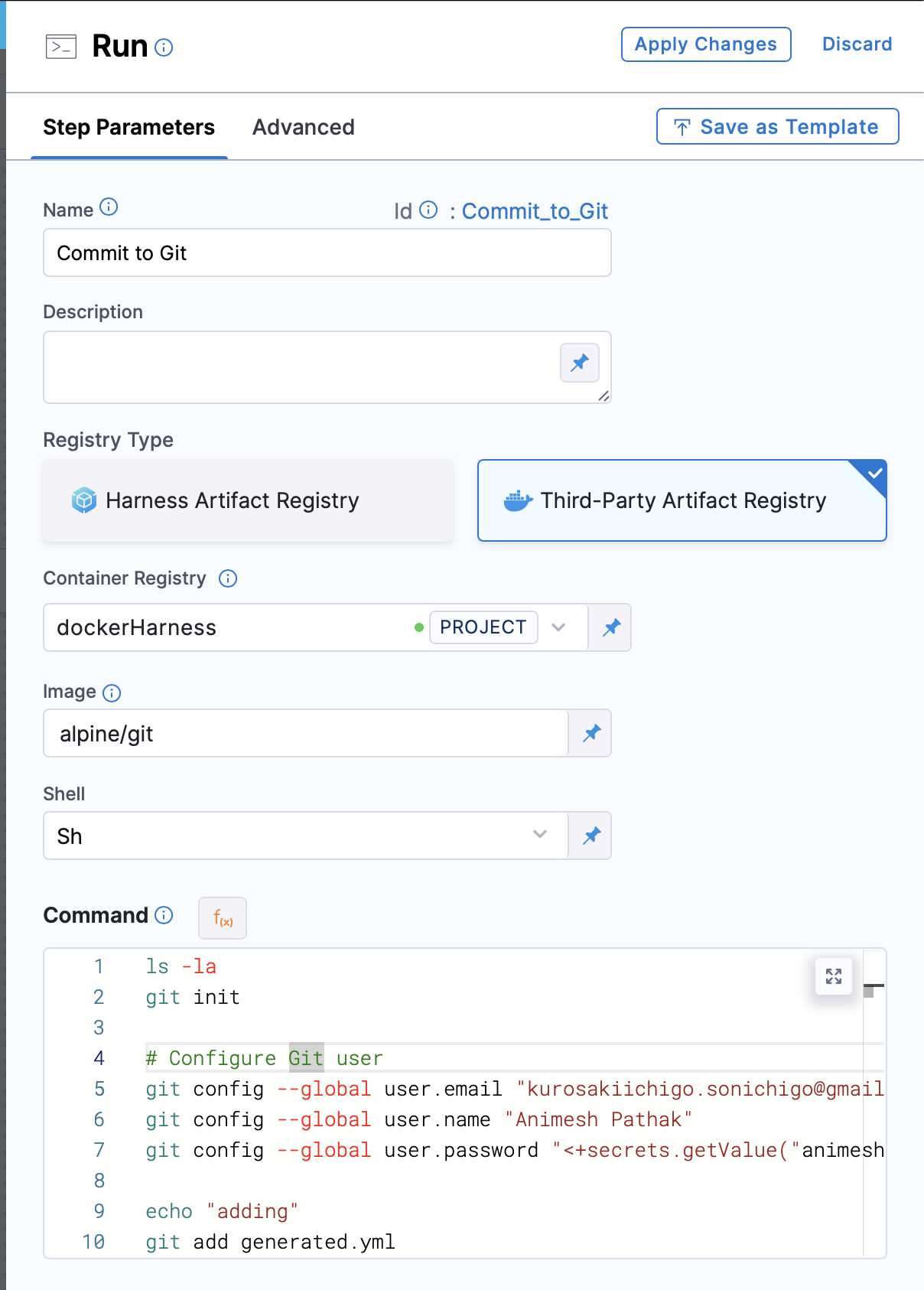
- Name: The name of the step.
- Registry Type: The type of registry to use. We can use
Third Party RegistryorHarness Artifact Registry. - Container Registry: The container registry to use. This is the location where the image is stored. In this case, we will use Docker Hub as the registry.
- Image: The name of the image to use. In this case, we will use
alpine/git. - Shell: The shell to use. We can use
bashorsh, depending on the image used. - Command: The command to be executed. In this case, we will use following command to commit the changelog file to the git repository:
git init
# Configure Git user
git config --global user.email <User Email>
git config --global user.name <User Name>
git config --global user.password <PAT Token> ## PAT saved in Harness Secrets Manager
git add generated.yml ## Our changelog file name which we generated in the previous step
git commit -m "generated changelog from running instance" -s
# Get current branch name
CURRENT_BRANCH=$(git rev-parse --abbrev-ref HEAD)
# Add remote repository
git remote add origin <User Email>:<PAT>@<Git Repo URL>.git ## Artifact Registry URL with https:// after @
# Push to remote using the current branch name
git push -u origin $CURRENT_BRANCH -f
- Click on
Apply Changes. Save the Pipeline and click on theRunbutton to run the pipeline.