Generating a MongoDB Changelog from an Existing Database
Harness Database DevOps enables teams to integrate database schema changes into Git-driven workflows.
When onboarding an existing MongoDB database, you can use the MongoDB.py Python script to extract the current schema and generate a Liquibase-compatible changelog.
This changelog can then be versioned in Git and used in subsequent deployments, ensuring auditability and consistency across environments.
By automating this process in a Harness pipeline, you can:
- Avoid manual changelog creation for legacy or existing databases
- Standardize schema tracking using Liquibase-compatible formats (JSON or YAML)
- Keep your database changes fully GitOps-compliant with version control and peer review
Prerequisites
Before implementing the pipeline, ensure the following:
- Pipeline execution environment can connect to your MongoDB instance
- The Git connector used in the pipeline has commit permissions
- MongoDB credentials have read-only access for schema extraction
Pipeline Implementation
Create a New Pipeline
- Go to your Harness pipeline.
- Click on "Create a Pipeline"
- In the Stage, select "Custom" and then create a "Step Group".
- Add the GitClone step.
- Then a new add step, Run
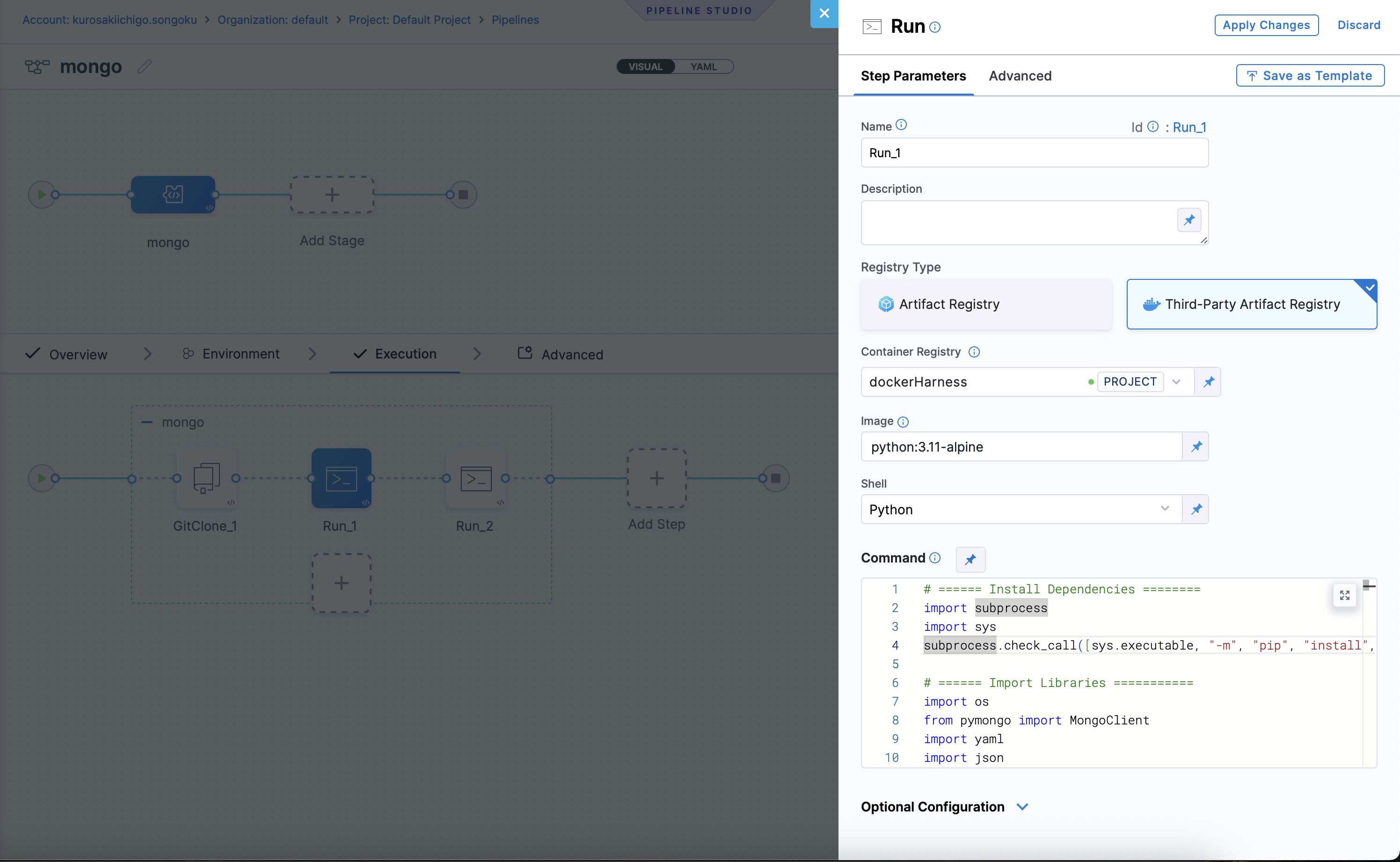
- Container Registry: used to pull images from private or public registries.
- Image: "python:3.11-alpine"
- Shell: "Python"
- Command: Add the following script under the command palette:
# ====== Install Dependencies ========
import subprocess
import sys
subprocess.check_call([sys.executable, "-m", "pip", "install", "pymongo", "pyyaml"])
# ====== Import Libraries ===========
import os
from pymongo import MongoClient
import yaml
import json
# === CONFIG ===
MONGO_URI = "mongodb://<username>:<password>@<host>:27017"
DATABASE_NAME = "test"
OUTPUT_FILE = "generated.yml"
AUTHOR = "Animesh" # Change as needed
CHANGESET_ID = "baseline-collections"
# === SETUP ===
client = MongoClient(MONGO_URI)
db = client[DATABASE_NAME]
collections = db.list_collection_names()
# === BUILD YAML STRUCTURE ===
changesets = []
for name in collections:
if(name=="DATABASECHANGELOGLOCK" or name=="DATABASECHANGELOG"):
continue
changes = []
# Add createCollection
collection_options = db[name].options()
changes.append({'createCollection': {'collectionName': name,'options':json.dumps(collection_options)}})
# Add createIndex for all non-_id indexes
indexes = db[name].index_information()
print("processing indexes for collection: "+name+"\r\n" + json.dumps(indexes))
for index_name, index_data in indexes.items():
if index_name == "_id_":
continue
index_fields = index_data['key']
index_for_changelog = {}
unique = index_data.get('unique',False)
for currentIndex in index_fields:
index_for_changelog.update({currentIndex[0]:currentIndex[1]})
change = {
'createIndex': {
'collectionName': name,
#'indexName': index_name, TODO: move to options
'keys': json.dumps(index_for_changelog) ,
'options': json.dumps({"name":index_name,"unique":index_data.get('unique',unique)})
}
}
if index_data.get('unique', False):
change['createIndex']['unique'] = True
changes.append(change)
changesets.append(
{'changeSet': {
'id': CHANGESET_ID+"-"+name,
'author': AUTHOR,
'changes': changes
}})
# Final YAML structure
changeset = {
'databaseChangeLog': changesets
}
# === WRITE TO FILE ===
with open(OUTPUT_FILE, "w") as f:
yaml.dump(changeset, f, sort_keys=False)
print(f"✅ YAML baseline changelog with indexes written to: {OUTPUT_FILE}")
In the above script:
- Update the
MONGO_URIto your MongoDB connection string. - Set the
DATABASE_NAMEto the name of your database. - Specify the
OUTPUT_FILEname as needed. - Change the
AUTHORandCHANGESET_IDvariables to reflect your changes.
Commit to Git Repository
You can commit the generated changelog file to your git repository using the Run Command step in the pipeline. This allows you to version control your changelog file and keep track of changes over time. Otherwise, once the pipeline is executed, pods will be deleted and the changelog file will be lost.
- In the Pipeline, under the
Step Groupsection, add a new stepRun Commandas the step type.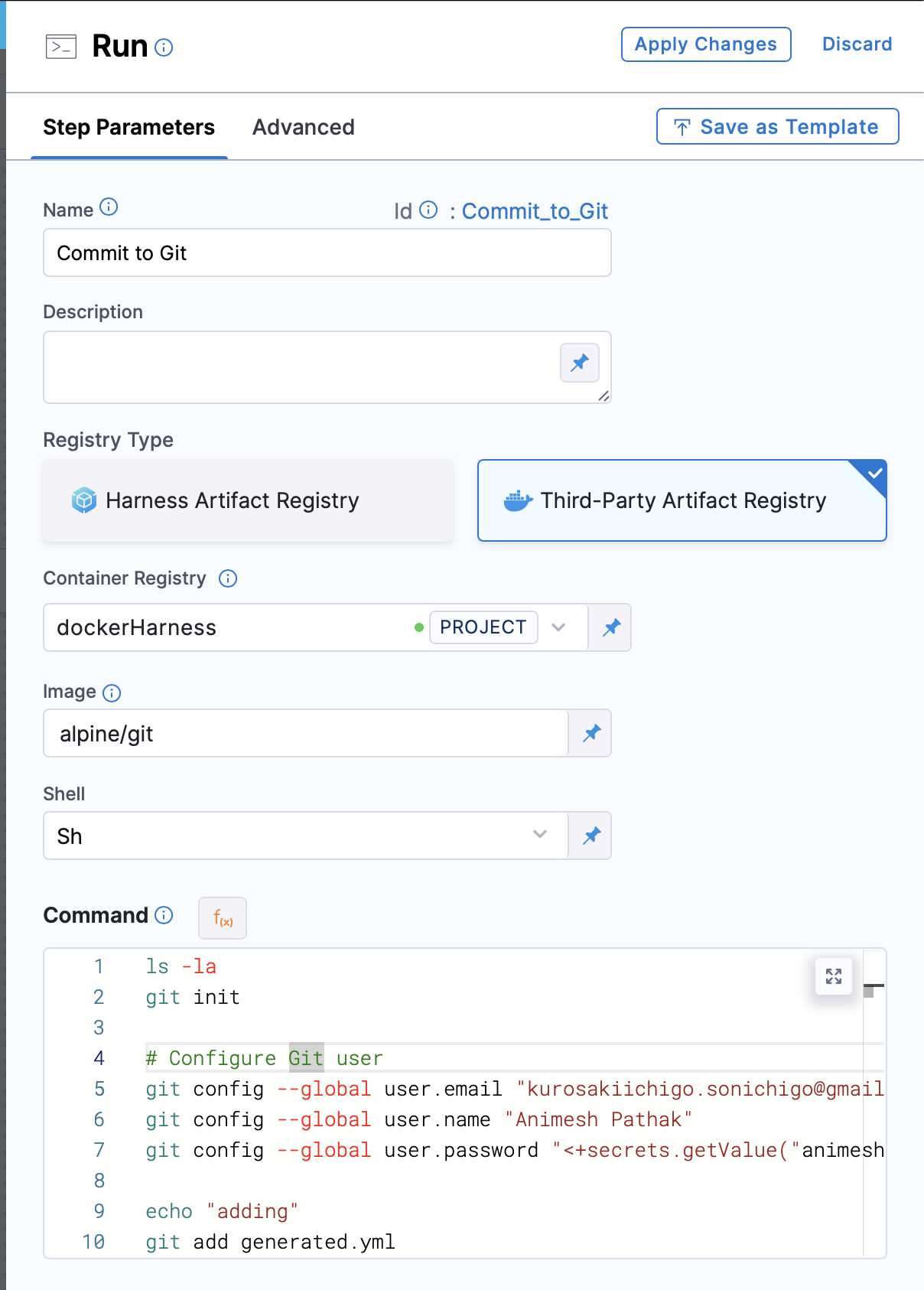
- Name: The name of the step.
- Registry Type: The type of registry to use. We can use
Third Party RegistryorHarness Artifact Registry. - Container Registry: The container registry to use. This is the location where the image is stored. In this case, we will use Docker Hub as the registry.
- Image: The name of the image to use. In this case, we will use
alpine/git. - Shell: The shell to use. We can use
bashorsh, depending on the image used. - Command: The command to be executed. In this case, we will use following command to commit the changelog file to the git repository:
git init
# Configure Git user
git config --global user.email <User Email>
git config --global user.name <User Name>
git config --global user.password <PAT Token> ## PAT saved in Harness Secrets Manager
git add generated.yml ## Our changelog file name which we generated in the previous step
git commit -m "generated changelog from running instance" -s
# Get current branch name
CURRENT_BRANCH=$(git rev-parse --abbrev-ref HEAD)
# Add remote repository
git remote add origin <User Email>:<PAT>@<Git Repo URL>.git ## Artifact Registry URL with https:// after @
# Push to remote using the current branch name
git push -u origin $CURRENT_BRANCH -f
- Click on
Apply Changes. Save the Pipeline and click on theRunbutton to run the pipeline.
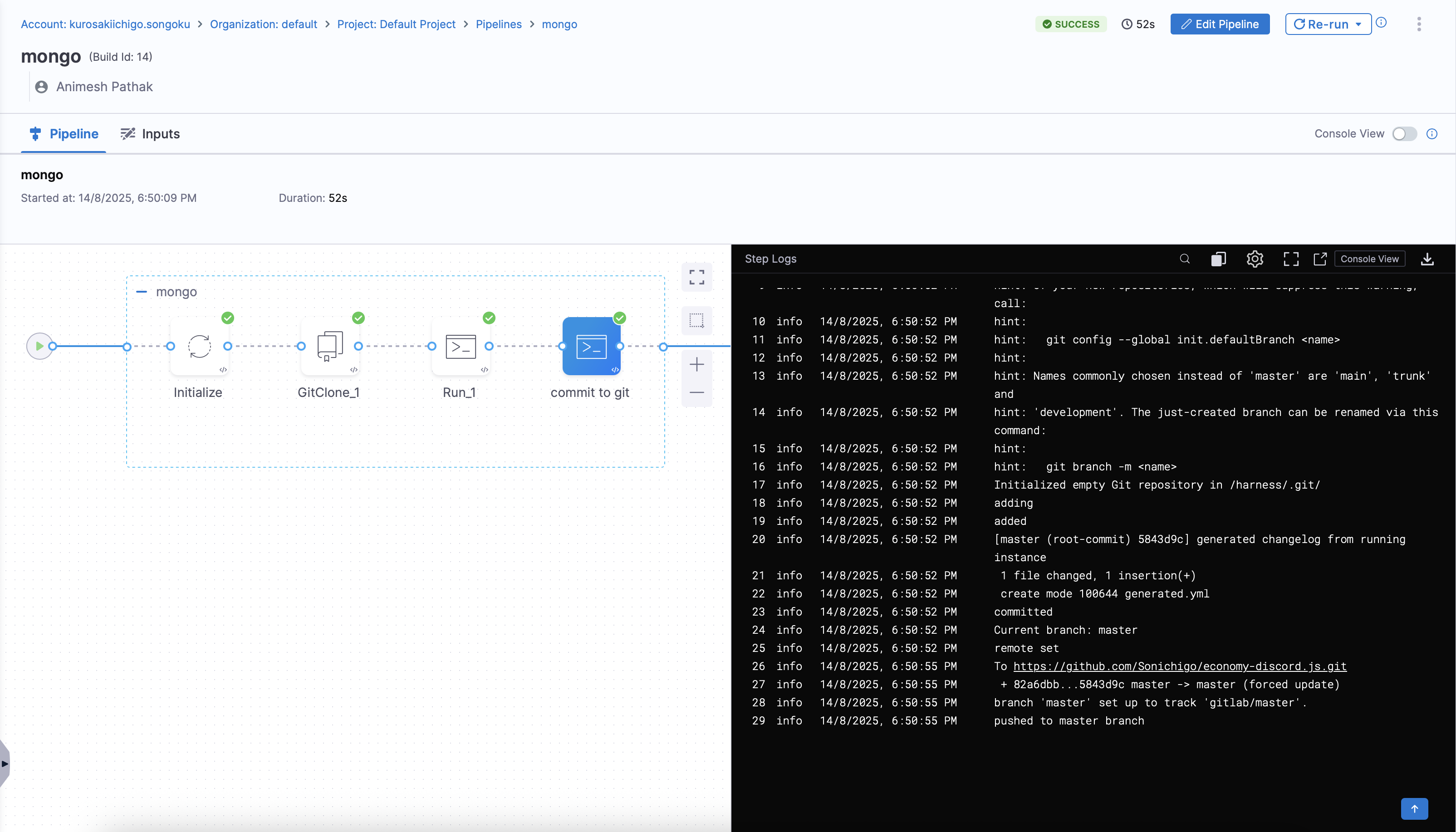 This step will ensure that the generated changelog file is committed to your Git repository, allowing you to track changes and maintain version control over your database schema changes.
This step will ensure that the generated changelog file is committed to your Git repository, allowing you to track changes and maintain version control over your database schema changes.
Best Practices
- Store changelogs in a dedicated folder (e.g.,
/db/changelog/) - Validate changelog generation in a staging pipeline before committing to production branches
- Parameterize connection details using Harness pipeline variables
- Always use a read-only MongoDB user for schema extraction By integrating this process into Harness pipelines, you ensure repeatable, auditable, and version-controlled database schema onboarding—a cornerstone of GitOps-driven database delivery.
FAQs
1. Can I change the changelog filename?
Yes. Update the OUTPUT_FILE variable in the script to set a custom filename.
2. Does it support JSON output instead of YAML?
Currently, the script outputs YAML. You can modify the yaml.dump section to use json.dump if JSON output is preferred.
3. How are indexes handled?
All non-_id indexes are included in the changelog with createIndex changes. The script preserves uniqueness flags.
4. How do I avoid including Liquibase internal collections?
The script automatically excludes DATABASECHANGELOG and DATABASECHANGELOGLOCK collections.